Structure of the book
Pieter van der Veen
How to start a new book
First the Pressbooks administrator has to create a user account for you.
Sign in
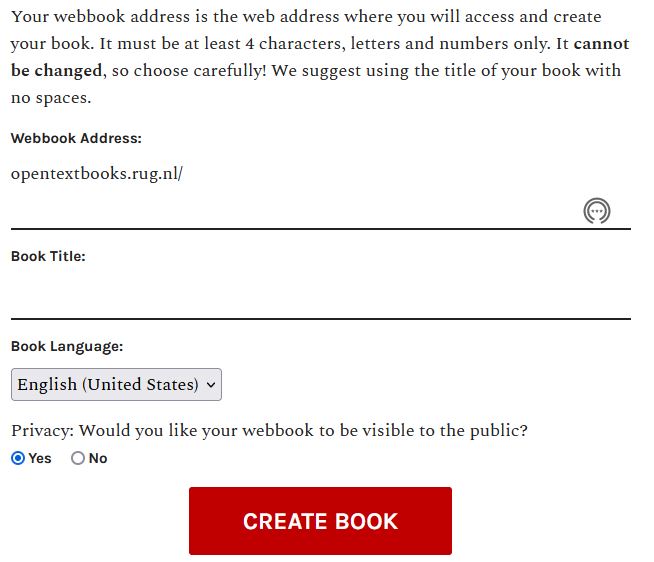
Click My books in the top navigation menu and click Create a new book
Create a webaddress using letters and numbers for example title of the book without spaces (cannot be changed )
Create a book title (can be adjusted later on in the process)
Adjust the privacy settings (while you are writing the book it is best to keep it private)
Create book
You can also have the book created for you by the Pressbooks admin.
On the Left you see the Menu, in the Middle your Workspace and on the Right the Statuspanel
Organize
- A book consists roughly of 4 parts:
- Frontmatter (introduction, acknowledgements etc.)
- Parts (naming can be adjusted via theme options, a part can also be invisible)
- Chapters (naming is optional)
- Backmatter (appendices, glossary, bibliography etc.)
Both the frontmatter and backmatter have a lot of options to change the type.
Front Matter
Book half title
Series title, frontispiece or blank
Title page
Copyright Page
Dedication
Epigraph
(Table of) Contents
(List of) Illustrations
(List of) Tables
Foreword
Preface
Acknowledgments (if not part of preface)
Introduction (if not part of text)
Abbreviations (if not in back matter)
Chronology (if not in back matter)
Back Matter
Acknowledgements (if not in front matter)
Appendix (or first, if more than one)
Second and subsequent appendixes
Chronology (if not in front matter)
Abbreviations (if not in front matter)
Notes
Glossary
Bibliography or References
(List of) Contributors
Illustration Credits (if not in captions or elsewhere)
Index(es)
Textboxes
There are 7 types of textboxes, most of them with an asociated sidebar
Standard
Shaded
Examples
Exercises
Key Takeaways
Learning objectives
Custom
If you have been added to an existing book as a author or editor.
- First add a chapter and create content
- Remember to save your chapter with the save button in the right menu
Textbook odd behaviour
- NOTE: Some textboxes can be a little temperamental; in particular the standard and shaded styles don’t like you hitting “Enter,” which will create a new textbox below the existing one. To get around this, you need to use a soft return by hitting “Shift+Enter” to get a new line. To delete a textbox remove the content with backspace and click delete.
The most important tools in the left menu are:
- Organize
- Book info
- Appearance
- Media
- TablePress
- H5P content
Text box with Sidebar
Learning objectives
Key elements
Exercises
Examples
This is an example of a custom box with my own CSS style attached. You can copy the css block from the Theme web styles and paste it into your web styles to avoid errors.
After that adjust the css, and paste the code in the Your web styles box under Themes/Custom Styles.
Pressbooks webbooks are designed to be accessible for users of all abilities and compatible with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
Pay special attention to the following practices:
- Use chapters, headings, and subheadings to organize content.
- Heading levels should represent the structure of the document.
- A Heading 1 is the document title or a main content heading. In Pressbooks, chapter titles will appear as H1 elements.
- A Heading 2 is a major section heading.
- A Heading 3 is a sub-section of the Heading 2.
- A Heading 4 is a sub-section of the Heading 3, and so on.
You should not skip heading levels, such as using a Heading 4 after a Heading 2 with no Heading 3 between the two.
- Use headings of an equal or higher rank to indicate the beginning of a new section, and headings with a lower rank to start a new subsection within the higher ranked section in which it occurs.
- Add alternative text to functional images that clearly describe the content.
- Check the color contrast for any images/figures included with your text and whenever using a shaded or colored background with text.
- When using links to other web content, include descriptive link text for the link. The link text should describe the content of the link; “our guide chapter on Navigation” is better than “click here” or “read more” as link text. If you are linking to non-web content (file downloads, for example) or causing a link to open in a new tab or window, consider telling the user this in the link description.
- When using tables, provide properly tagged table titles/captions and table headers/footers where appropriate, and avoid using merged or split cells wherever possible.
- Include captions and/or transcripts for any multimedia you include with your text.
vdvdvdv